Intermediate Action Required – Internal Documentation
The Intermediate Action Required dashboard is designed to help teams proactively identify and resolve operational and system issues across inventory, orders, users, and sales performance. This document provides a detailed explanation of each action section, including the purpose, data fields, filters, and step-by-step instructions for taking necessary actions. The goal is to help ensure profitability, improve user experience, and maintain operational integrity.
1. Inventory Cost Issues
This section highlights a critical issue where the cost of goods (COG) for inventory items is higher than the current selling price. Selling products below cost leads to direct financial losses and must be addressed either through price correction, promotional adjustments, or vendor negotiations.
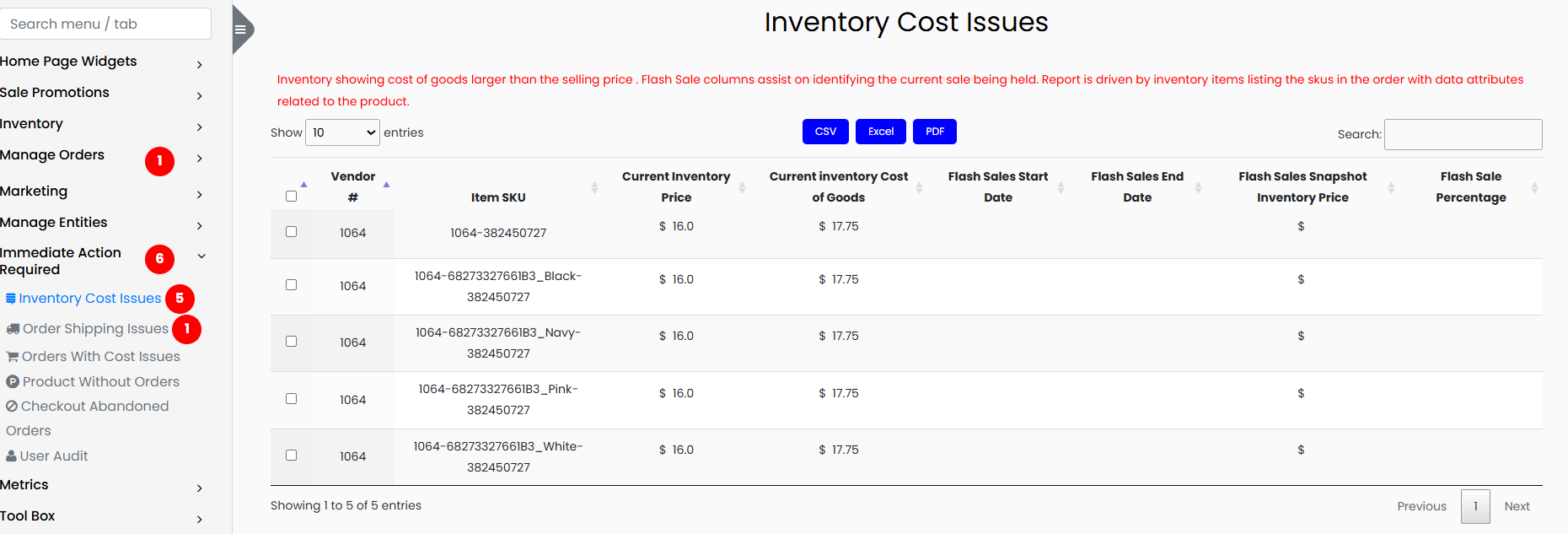
The data in this section is presented by SKU and includes the following fields:
- Vendor Number
- Item SKU
- Current Inventory Price
- Current Inventory Cost of Goods
- Flash Sale Start Date
- Flash Sale End Date
- Flash Sales Snapshot Inventory Price
- Flash Sale Percentage
Steps to Review and Resolve
- Review the list of SKUs where the current inventory cost of goods exceeds the inventory price.
- Check if the item is part of a flash sale by verifying the flash sale start and end dates.
- If the price discrepancy is due to an active sale, confirm it is intentional and documented.
- If not related to a sale, investigate reasons such as incorrect pricing or increased supplier costs.
- Work with the pricing or category management team to adjust prices or renegotiate vendor terms.
2. Orders with Shipping Issues
This section identifies items that have not been shipped in multiple orders, indicating potential inventory issues, vendor problems, or warehouse errors.
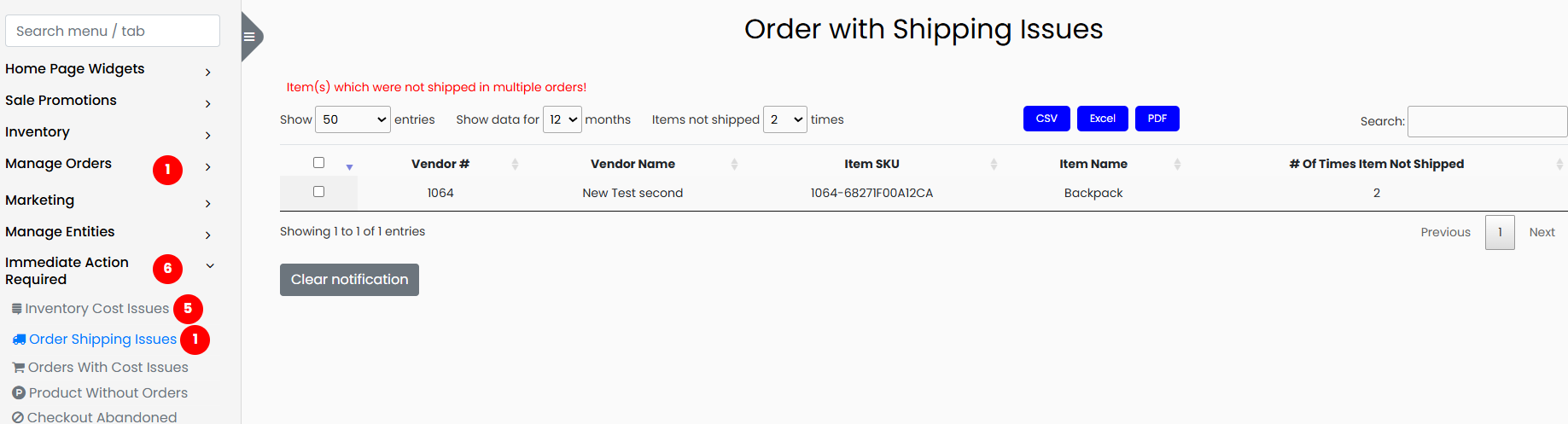
The data includes:
- Vendor Number
- Vendor Name
- Item SKU
- Item Name
- Number of Times Item Not Shipped
Steps to Review and Resolve
- Filter the report to show data for the past 12 months.
- Identify items that have not been shipped two or more times.
- Cross-check warehouse inventory records to confirm product availability at order time.
- Investigate fulfillment issues with vendors or internal warehouse teams.
- If recurring, consider updating product availability status or sourcing alternative suppliers.
- Monitor future orders to confirm resolution of the issue.
3. Orders with Cost Issues
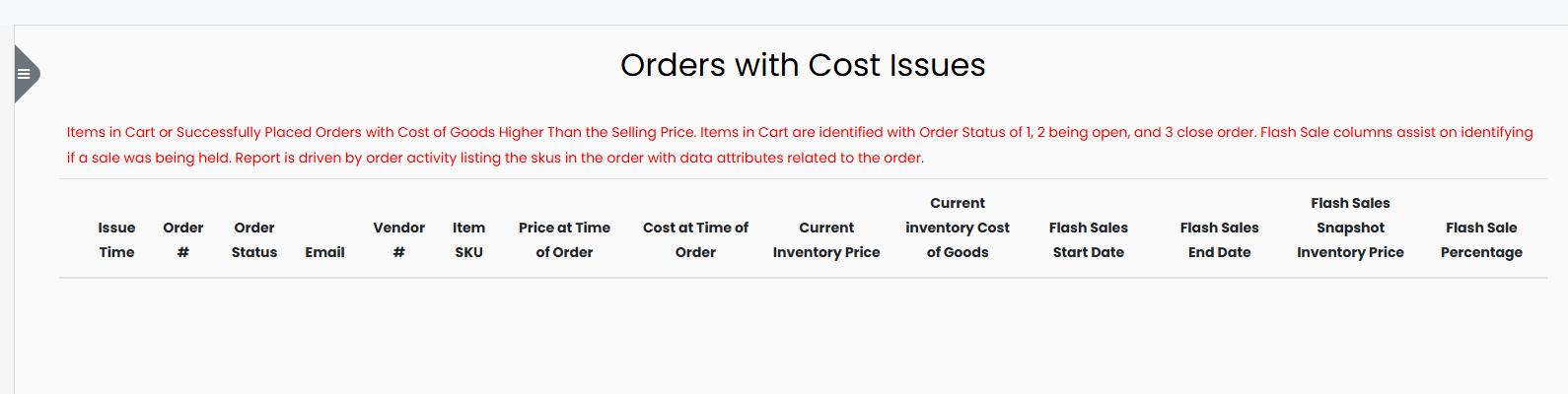
This section lists items in customer carts or placed orders where the cost of goods is higher than the selling price. This negatively impacts profit margins and should be corrected.
Order status codes:
- 1: Cart (in progress)
- 2: Open Order (not yet completed)
- 3: Closed Order (completed transaction)
Data fields include:
- Issue Time
- Order Number
- Order Status
- Customer Email
- Vendor Number
- Item SKU
- Price at Time of Order
- Cost at Time of Order
- Current Inventory Price
- Current Inventory Cost of Goods
- Flash Sale Start Date
- Flash Sale End Date
- Flash Sales Snapshot Inventory Price
Steps to Review and Resolve
- Filter the report to display data for the last 30 days.
- Focus on closed orders (status
3) where the cost is higher than the price. - Check if a flash sale influenced the lower price and confirm the pricing was approved.
- For carts (status
1), identify whether price mismatches are preventing purchases. - Work with pricing or product teams to fix incorrect pricing.
- Implement automated checks to prevent future cost-price mismatches.
4. Products Without Orders
This report shows products that have not received any orders within a specified period, such as 30 days. These items may indicate poor visibility, demand, or performance.
Included fields:
- SKU Number
- Vendor SKU Number
- Quantity Available
- Short Description
- Vendor Number
- Brand Name
- Model Name
Steps to Review and Resolve
- Select the timeframe to review (e.g., 30 days).
- Identify SKUs with no order activity during that period.
- Confirm the items are live and visible on the platform.
- Evaluate the marketing and merchandising status of the items.
- Consider price adjustments, bundles, or promotions to stimulate sales.
- For consistently underperforming products, consider delisting or liquidating inventory.
5. Checkout Abandoned Orders
This section identifies customer carts that were started but never completed. Analyzing abandoned checkouts helps improve conversion and detect possible checkout issues.
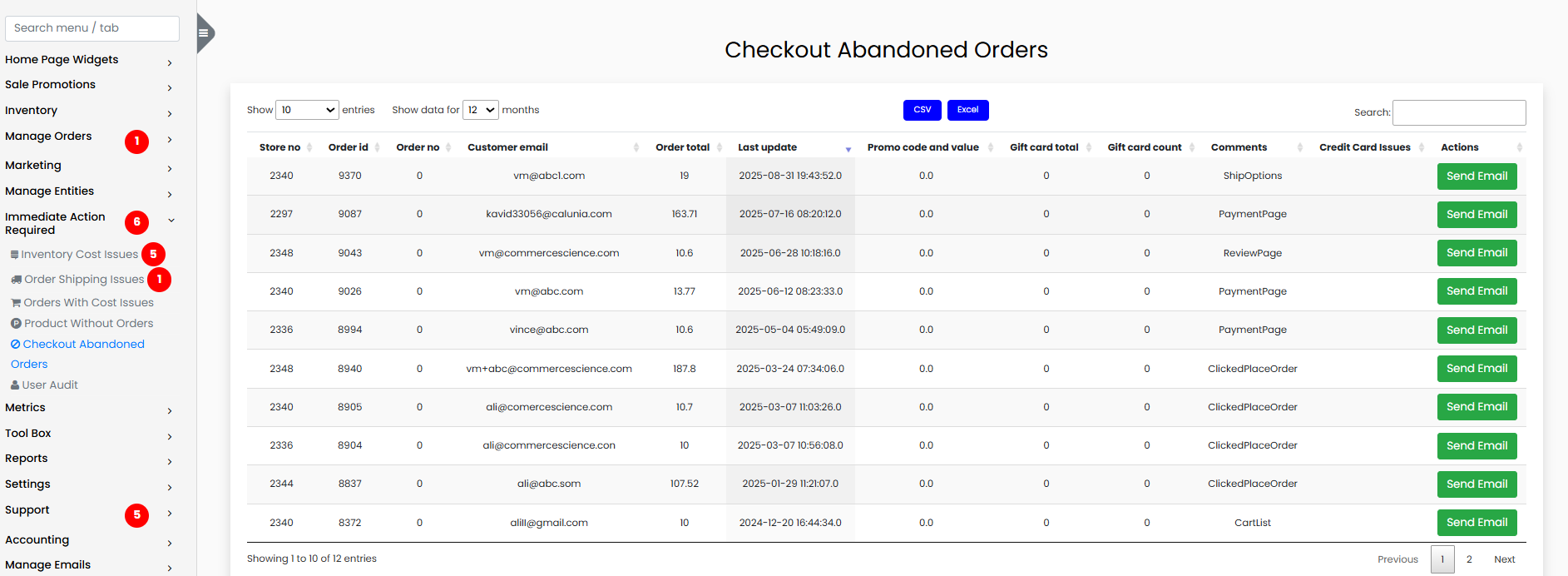
The report includes:
- Store Number
- Order ID
- Order Number
- Customer Email
- Order Total
- Last Update
- Promo Code and Value
- Gift Card Total and Count
- Customer Comments
- Credit Card Issues
Steps to Review and Resolve
- Filter data to view results from the past 12 months.
- Look for patterns such as specific products or promotions causing abandonment.
- Read customer comments for insight into failed checkout experiences.
- Investigate any credit card-related issues in the logs.
- Collaborate with UX or dev teams to improve checkout performance.
- Use email remarketing or retargeting campaigns to recover lost orders.
6. Manage User Audit
This section is used to audit user access to the platform. It helps ensure that user accounts are correctly enabled or disabled across both the AWS infrastructure and the platform database.
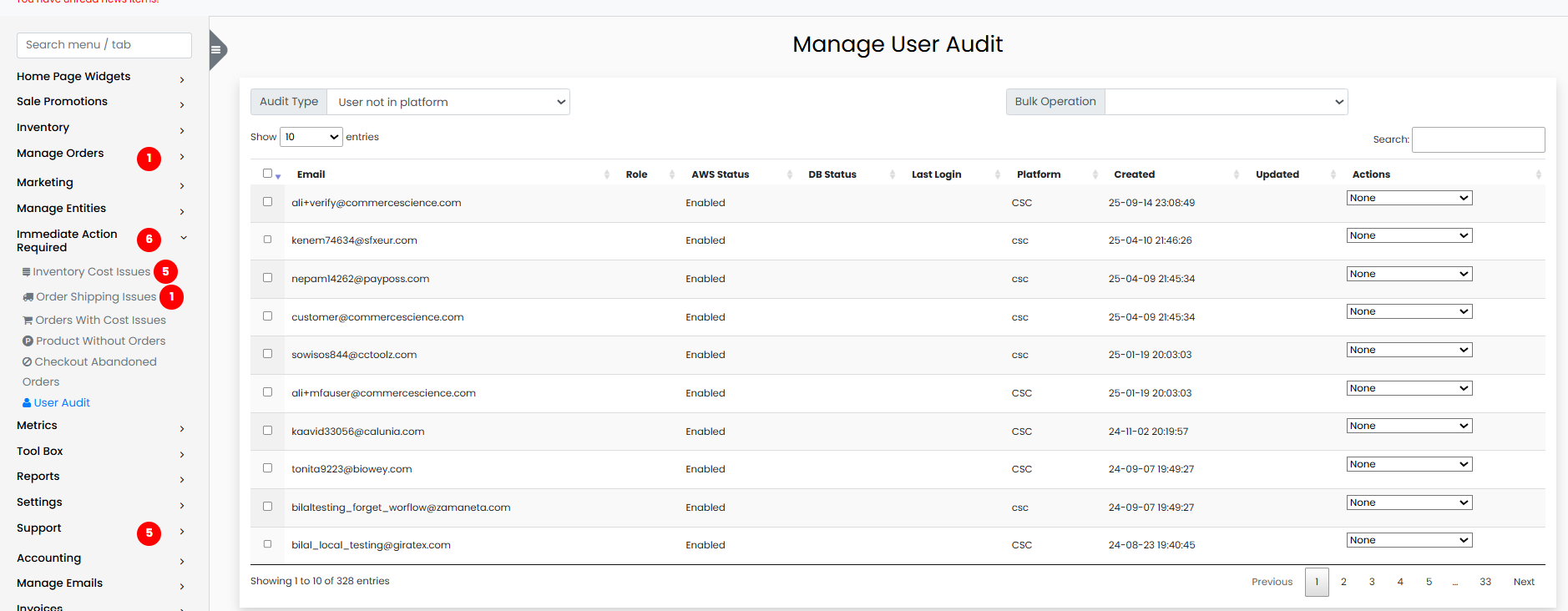
The report includes:
- Email Address
- Role
- AWS Status
- Database Status
- Last Login
- Platform Type (Admin, Vendor Portal, etc.)
- Account Creation Date
- Last Updated
Audit Types: - User not found in platform - User disabled in platform - Bulk user operations
Available Actions
- Disable in AWS: Disables the user in AWS IAM.
- Enable in AWS: Reactivates a previously disabled user in AWS.
- Delete from AWS: Completely removes the user from AWS.
- Disable in Database: Prevents login on the platform while keeping account data.
- Delete from Database: Removes the user's record from the application database.
- Delete from AWS and DB: Fully deletes the user from both AWS and platform databases.
Steps to Review and Take Action
- Use filters to select the desired audit type.
- For each user, cross-check AWS and DB status to identify inconsistencies.
- Confirm whether the user should still have access.
- Take appropriate action using the listed buttons or bulk operation tools.
- Double-check user role and history before deleting any user account.
- For large updates, use bulk operation mode with caution and review logs afterward.
General Recommendations
- Monitor this dashboard regularly to identify issues early.
- Use filters and search tools to narrow your focus to the most critical problems.
- Work collaboratively across departments (support, warehouse, pricing, security).
- Export data as needed for reporting or offline analysis.
- Use automation where possible to detect anomalies such as cost issues or unshipped orders.